The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) has released a new report on household consumption expenditure in India, revealing a significant increase in spending over the past decade. This blog post summarizes the key findings and their implications.
Key Points:
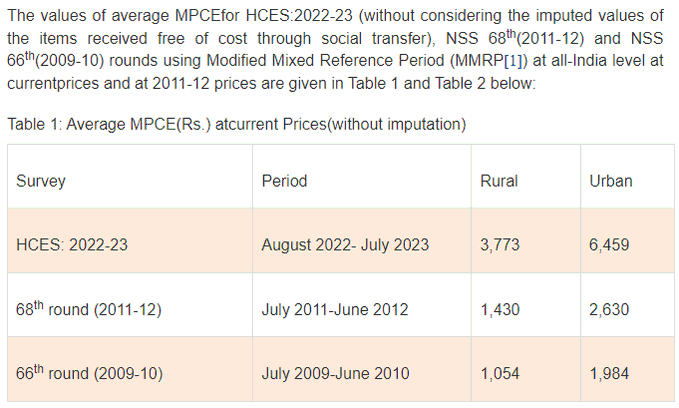
- Per capita monthly household consumption expenditure (MPCE) has more than doubled between 2011-12 and 2022-23. This translates to an average monthly spend of Rs. 3,773 in rural areas and Rs. 6,459 in urban areas, as of 2022-23.
- The survey considers both paid and free goods and services. This includes items received through government welfare programs like the National Food Security Act (NFSA) and Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana (PMGKAY) for food, and laptops, tablets, and school supplies for education.
- The increase in spending is higher in rural areas compared to urban areas. This suggests a potential narrowing of the urban-rural spending gap, potentially indicating improved living standards in rural communities.
- The data is adjusted for inflation to provide a more accurate picture of changes in real spending power. This allows for comparisons across different time periods.
Implications:
- The rise in household spending points towards an improved economic climate in India, with individuals and families having more disposable income.
- The increased spending in rural areas suggests a potential improvement in living standards for rural communities, potentially due to government initiatives and economic growth.
- The inclusion of free goods and services provides a more comprehensive picture of household consumption, taking into account government welfare programs and their impact on living standards.
